I. Application Solutions for Surgical Consumables
(1) Surgical Sutures
Surgical sutures are made from water-soluble nonwoven fabrics with high strength and excellent biocompatibility. During the surgical procedure, these sutures can suture wounds as precisely as traditional sutures, ensuring that the wound edges are closely approximated. After the operation, as the wound heals, the sutures gradually dissolve under the action of human tissue fluid. There is no need for a suture removal operation, which not only reduces the pain and infection risk for patients but also decreases the workload of medical staff. For example, in surgeries with high aesthetic requirements after recovery, such as ophthalmic and plastic surgeries, water-soluble nonwoven surgical sutures leave no residue after dissolution, avoiding scarring caused by suture removal and improving the patient's recovery outcome.
(2) Surgical Pads
Water-soluble nonwoven fabrics are made into surgical pads for the isolation and protection of surgical sites. In some complex surgeries, surgical pads can be placed between tissues and surgical instruments to prevent the instruments from damaging the surrounding tissues. After the surgery is completed, the surgical pads gradually dissolve through specific irrigation solutions or the body's own physiological environment, eliminating the need for additional removal and reducing the risk of surgical residues. For instance, in coronary artery bypass grafting surgery, using water-soluble nonwoven surgical pads can effectively reduce the friction and damage of instruments to cardiac tissues, and their dissolution does not affect postoperative recovery.
II. Application Solutions for Medical Packaging
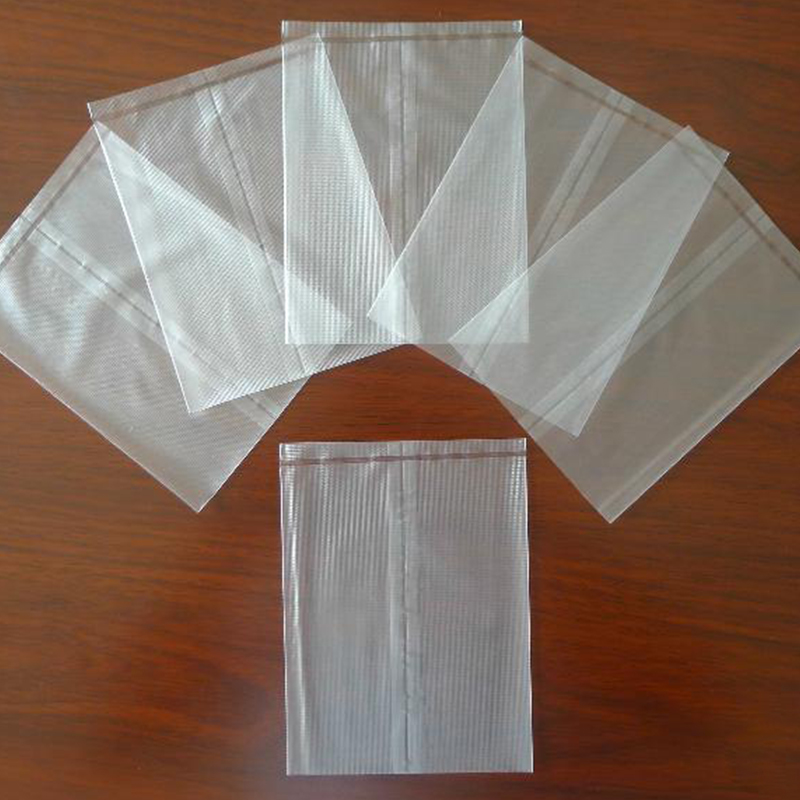
(1) Packaging for Sterilized Instruments
Water-soluble nonwoven fabrics are used to package medical devices that need to be sterilized. During sterilization processes such as high-temperature and high-pressure steam sterilization or low-temperature plasma sterilization, water-soluble nonwoven fabrics can withstand the sterilization environment and effectively protect the devices from contamination. When the devices are delivered for clinical use, the packaging and the devices are directly placed in water, and the water-soluble nonwoven fabric dissolves rapidly, facilitating the access of medical staff to the devices and reducing the operation process. This packaging method avoids the particulate contamination that may occur during the removal of traditional packaging materials, ensuring the cleanliness of the devices. It is suitable for packaging various precision surgical instruments.
(2) Pharmaceutical Packaging
For some special oral medications or topical preparations, independent packaging is made from water-soluble nonwoven fabrics. When using the medications, patients can take the drugs or apply the preparations together with the packaging directly. The packaging dissolves in the body or at the affected area, releasing the drugs. This packaging method not only ensures the stability and tightness of the drugs but also makes it convenient for patients to use. Meanwhile, it reduces the generation of packaging waste, which is in line with the concept of environmental protection. For example, effervescent tablets for children are packaged with water-soluble nonwoven fabrics. Children can directly drop the tablets with the packaging into a glass of water, and the packaging dissolves, allowing the drugs to dissolve for drinking, which is simple and convenient.
III. Application Solutions for Wound Care
(1) Wound Dressings
Water-soluble nonwoven fabrics with good water absorption and air permeability are made into wound dressings. When the dressings are applied to the wound, they can quickly absorb wound exudate, maintaining a moist environment at the wound site and promoting wound healing. Moreover, the adhesion of water-soluble nonwoven fabrics to the wound tissue is moderate, preventing the dressings from sticking to the wound during dressing changes and reducing patient discomfort. As the wound gradually heals, the water-soluble nonwoven fabric dressings can be gradually dissolved through rinsing or soaking with normal saline, eliminating the need for forced removal and reducing the risk of secondary damage. Water-soluble nonwoven wound dressings have significant advantages in treating hard-to-heal wounds such as large - area burns and chronic ulcers.
(2) Drug Sustained-Release Carriers
Antibiotics, growth factors, and other drugs are loaded into water-soluble nonwoven fabrics to make drug - sustained-release dressings. After these dressings are applied to the wound, as the water-soluble nonwoven fabrics dissolve slowly, the drugs are continuously released to the local wound area, achieving long - acting drug effects and improving the treatment outcome. For example, when treating infected wounds, water-soluble nonwoven dressings containing antibiotics can continuously release antibiotics over a period of time, inhibiting bacterial growth, accelerating wound healing, and reducing the systemic dosage of drugs, thereby minimizing drug side effects.
IV. Auxiliary Solutions for Medical Waste Treatment
During the classification and collection of medical waste, special waste packaging bags are made from water-soluble nonwoven fabrics. For some infectious medical waste, such as disposable syringes and gauze, after being placed in water-soluble nonwoven packaging bags, the bags dissolve rapidly through high-temperature and high-pressure steam treatment and are then subjected to harmless treatment together with the medical waste. This approach avoids the environmental pollution problems that may occur during the treatment of traditional plastic packaging bags, simplifies the medical waste treatment process, improves treatment efficiency, and reduces the risk of leakage of medical waste during transportation and storage.




 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Türk
Türk