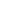
Understanding PO Hot-Melt Adhesive Film and Its Core Advantages
Polyolefin (PO) hot-melt adhesive film represents a significant advancement in bonding technology, offering a clean, efficient, and strong method for joining a wide array of materials. Unlike liquid adhesives, this thermoplastic film is solid at room temperature and activates upon the application of heat and pressure, flowing into the substrates to create a powerful, permanent bond upon cooling. Its growing popularity is attributed to a unique combination of properties that make it suitable for demanding applications across various industries.
Key Characteristics and Benefits
The fundamental appeal of PO hot-melt adhesive film lies in its well-balanced property profile. It is engineered to provide consistent performance, which is critical for both manufacturing processes and the final product's durability.
- Versatile Bonding: It effectively bonds diverse materials, including many plastics, metals, glass, and textiles, that are often challenging to join with other adhesive types.
- Clean and Solvent-Free: As a 100% solid material, it contains no solvents or water, eliminating concerns about volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, drying times, or shrinkage, resulting in an environmentally friendlier process.
- Excellent Resistance: PO-based films exhibit strong resistance to water, chemicals, and UV degradation, ensuring the longevity of the bond even in harsh environmental conditions.
- Ease of Application: The film format allows for precise pre-placement of adhesive, minimizing waste and mess. The activation process is fast, facilitating high-speed production lines and improving overall manufacturing efficiency.
- Consistent Performance: Manufactured to tight tolerances, the film provides a uniform thickness and adhesive distribution, guaranteeing consistent bond strength and quality across every production run.
Comparing PO Hot-Melt to Other Adhesive Films
While all hot-melt adhesive films share the basic principle of thermal activation, the base polymer chemistry dictates their specific performance. PO films occupy a distinct position compared to other common types like Polyurethane (PU) or Polyamide (PA).
For instance, when compared to PU hot-melt films, PO films generally offer superior moisture resistance and at a lower cost, making them ideal for applications exposed to damp environments. However, PU films typically provide better flexibility and a wider range of elasticit. Conversely, compared to PA films, which are known for exceptional high-temperature resistance, PO films offer a more balanced cost-to-performance ratio for medium-duty applications and excel in bonding low-surface-energy plastics. The following table outlines these key differences in a structured format.
| Property | PO Hot-Melt Film | PU Hot-Melt Film | PA Hot-Melt Film |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Good | Moderate to Poor |
| Flexibility / Elasticity | Good | Excellent | Fair (Can be brittle) |
| Heat Resistance | Good | Fair to Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Cost | Moderate | Higher | Higher |
| Best For | Moist environments, LSE plastics, cost-sensitive apps | Flexible laminates, textiles | High-temperature applications |
This comparison clearly demonstrates that PO hot-melt film is not a universal solution but is exceptionally well-suited for specific scenarios where its balance of moisture resistance, chemical stability, and cost-effectiveness provides a significant advantage.
Key Applications of PO Hot-Melt Adhesive Film
The unique property set of PO hot-melt adhesive film makes it a preferred choice for a multitude of industrial and commercial bonding applications. Its ability to create strong, durable, and invisible bonds has revolutionized assembly processes in several sectors.
Automotive Interior Assembly
Modern automotive interiors are a complex assembly of various materials, including fabrics, foams, plastics, and thin metals. PO hot-melt adhesive film is extensively used in this domain for laminating interior trim components. It is ideal for bonding door panel coverings, headliners, trunk liners, and instrument panel skins. The film provides a clean and fog-free bond, which is crucial for passenger cabin air quality. Its resistance to temperature fluctuations and plasticizer migration (common in vinyls and synthetic leathers) prevents delamination over the vehicle's lifespan, even in extreme climates. The process is also highly automated, allowing for rapid production rates in manufacturing plants.
Textile and Apparel Manufacturing
In the textile industry, breathable PO hot-melt adhesive film has become a game-changer, particularly in the production of technical outerwear and protective clothing. This specific type of film is micro-porous, allowing water vapor (sweat) to escape from inside the garment while simultaneously blocking liquid water from entering from the outside. This property is essential for creating comfortable and functional waterproof yet breathable apparel. The film is used to seam-seal jackets, pants, and gloves, replacing traditional sewing and taping methods with a stronger, more durable, and entirely waterproof bond that does not require needle holes that can leak.
Specialized Niche Applications
Beyond these major industries, PO hot-melt films find use in several specialized niches. One growing area is in the construction and home furnishings sector for bonding decorative laminates to panels for furniture and fixtures. Another critical application is in the electronics industry, where specific grades of film are used for low temperature PO adhesive film applications to bond heat-sensitive components or displays without causing thermal damage. Furthermore, the material is crucial in creating composite structures for aerospace and marine applications, where its weight-saving properties and resistance to moisture are highly valued. For bonding challenging substrates, PO adhesive film for difficult to bond plastics such as polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) is often the only effective solution, enabling new design possibilities in product engineering.
Selecting the Right PO Hot-Melt Adhesive Film
Choosing the appropriate PO hot-melt adhesive film is paramount to achieving a successful and durable bond. The selection process should not be based on cost alone; it requires a careful analysis of the application requirements and the film's technical specifications.
Critical Performance Parameters
Several key parameters must be evaluated to ensure compatibility and performance. Ignoring any of these factors can lead to bond failure.
- Melting Point (Melt Flow Index): The temperature at which the film activates must be compatible with the heat tolerance of the substrates being bonded. A film with too high a melt point could damage sensitive materials.
- Bonding Strength (Peel & Shear Strength): The required strength of the final bond is a primary consideration. Technical datasheets provide peel and shear strength values, which should be matched to the mechanical demands of the application.
- Substrate Compatibility: The film must be chemically compatible with the materials it is bonding. This is especially critical for PO adhesive film for difficult to bond plastics which often have low surface energy. Surface treatment might be necessary in some cases.
- Flexibility and Elongation: If the final product will be flexed or bent, the adhesive film must have sufficient elongation to withstand these stresses without cracking or debonding.
- Environmental Resistance: The application environment dictates the need for resistance to UV light, humidity, chemicals, or temperature extremes. PO films generally perform well, but specific formulations are optimized for particular challenges.
Understanding Formats and Application Methods
PO hot-melt adhesive films are available in different formats to suit various application methods and production scales.
Supported vs. Unsupported Films
Films are categorized as either supported or unsupported. Unsupported films are a pure layer of adhesive, offering high clarity and a soft hand feel, ideal for textile lamination. Supported films incorporate a scrim or carrier material (e.g., a light non-woven or woven fabric) within the adhesive layer. This carrier adds dimensional stability, tear strength, and gap-filling properties, making them suitable for bonding uneven surfaces or for applications requiring higher ultimate strength.
Application Techniques
The primary application method involves using a heat press for flat laminates or a continuous roll laminator for high-volume production. For large or complex 3D shapes, specialized equipment that can apply heat and pressure conformally is used. The process typically involves placing the film between the two substrates, applying heat to melt the film, applying pressure to ensure intimate contact and wetting, and then cooling under pressure to solidify the bond. For projects requiring customization, custom die cut PO hot-melt film is available, which is pre-cut into specific shapes to minimize waste and streamline the assembly process, such as in automotive trim or electronic device assembly.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Application
Even with the right material selected, achieving a perfect bond requires attention to process details. Several common challenges can arise during the application of PO hot-melt adhesive film.
Inadequate Bond Strength
If the bond is not achieving the expected strength, the root cause is often related to the lamination process parameters. The three key factors—temperature, pressure, and time—must be optimized.
- Temperature: If the temperature is too low, the film will not achieve full melt and flow, preventing proper wetting of the substrate surface. If it is too high, it can degrade the adhesive polymer or damage the substrate.
- Pressure: Insufficient pressure will not force the liquefied adhesive into the microscopic pores of the substrate surface, resulting in poor adhesion. Excessive pressure can squeeze too much adhesive out of the bond line or distort the substrates.
- Time: The dwell time must be long enough to allow the entire film and the substrate interface to reach the necessary temperature and for the adhesive to flow. Cooling time under pressure is equally critical to form a strong, crystalline structure.
Conducting small-scale trials to create a Design of Experiments (DOE) is the best practice for dialing in these parameters for any new application.
Addressing Substrate Surface Issues
The surface condition of the material being bonded is a frequent culprit in adhesion problems. Contaminants like oil, dust, release agents, or moisture can create a weak boundary layer. For polymers with very low surface energy, such as PP and PE, the surface often requires pretreatment to increase its energy and allow the adhesive to wet it effectively. Corona treatment, plasma treatment, or flame treatment are common industrial methods used to prepare these difficult to bond plastics for successful lamination with PO adhesive film. Ensuring substrates are clean, dry, and properly treated is a fundamental step that cannot be overlooked.
The Future and Innovation of PO Hot-Melt Technology
The field of hot-melt adhesives is not static; it is continuously evolving to meet new challenges and opportunities. Research and development are focused on enhancing the performance and sustainability of PO hot-melt adhesive films.
Trends in Material Science
Future innovations are likely to focus on developing films with even higher performance characteristics, such as enhanced heat resistance to withstand lead-free soldering processes in electronics or improved adhesion to an ever-wider range of innovative composite materials. The development of ultra-thin PO hot-melt adhesive film is another significant trend, driven by the miniaturization of electronics and the demand for lighter, thinner consumer products. These ultra-thin films provide strong bonding without adding noticeable thickness or weight, which is critical in devices like smartphones, wearables, and flexible displays.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The adhesive industry is increasingly focused on sustainability. For PO hot-melt films, this involves several avenues. Firstly, the development of bio-based polyolefins derived from renewable resources is gaining traction. Secondly, there is a push towards creating thermally reversible or recyclable adhesive systems that allow for easier disassembly and recycling of products at the end of their life cycle. Finally, the solvent-free nature of the film.




 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Türk
Türk